Query Language
ObjectQuel draws inspiration from QUEL, the pioneering query language from UC Berkeley's Ingres project. Unlike SQL's table-centric approach, ObjectQuel queries work directly with your domain entities using object-oriented syntax. Queries read naturally while leveraging powerful search capabilities including wildcards, regex, and full-text search.
Query Structure
Every ObjectQuel query follows this structure, with clauses written in this specific order:
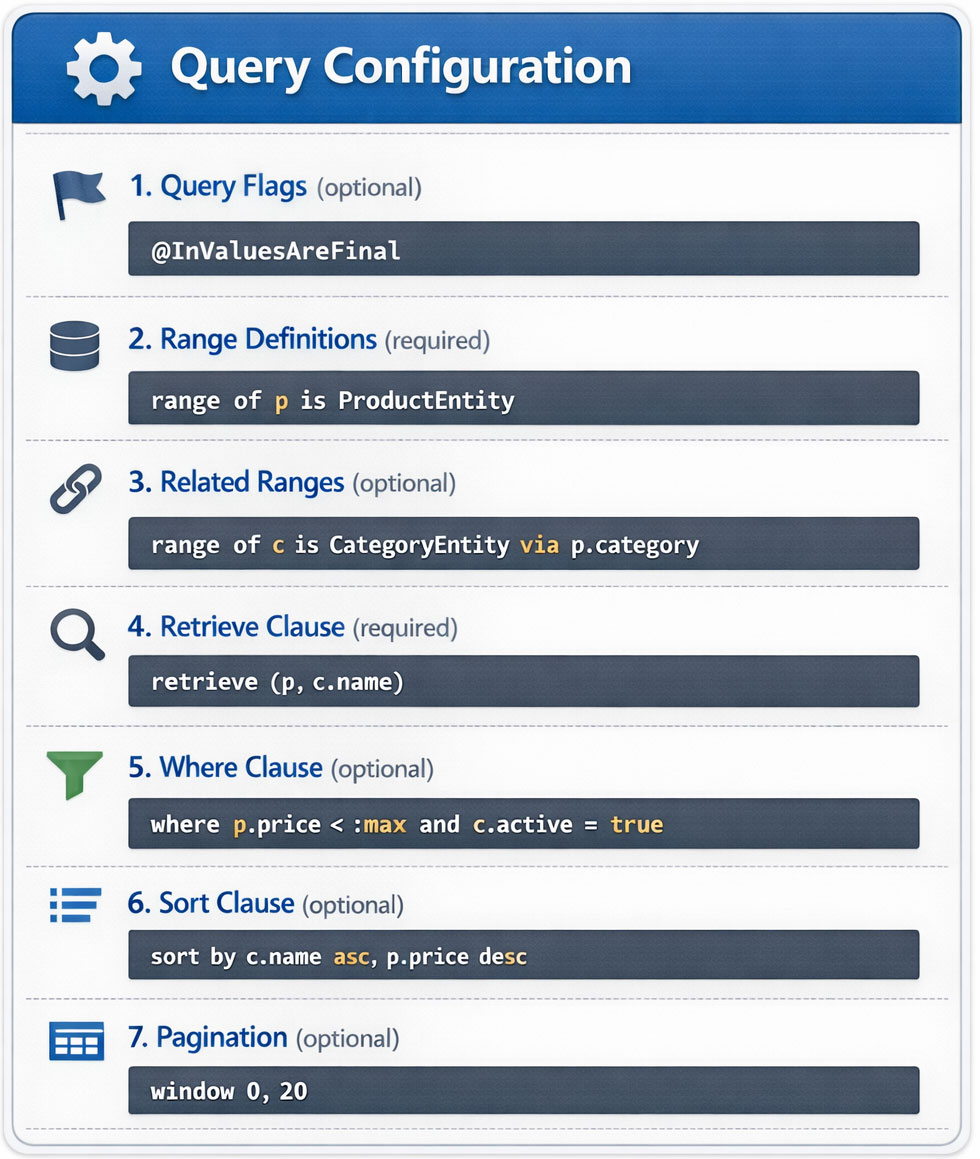
Query Optimization Flags
Query flags modify execution behavior for specific optimization scenarios. Flags are placed before the first range definition.
@InValuesAreFinal
When you query using an IN clause on primary keys or unique identifiers, ObjectQuel normally cannot assume how many rows will match — the same ID might appear in a non-unique column, or the query planner may not know the column is unique. The @InValuesAreFinal flag tells ObjectQuel that each value in the IN clause will match at most one row, enabling it to stop scanning early once all values have been found:
$results = $entityManager->executeQuery("
@InValuesAreFinal
range of p is App\\Entity\\ProductEntity
retrieve (p) where p.productId in (:ids)
", ['ids' => [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]]);When to use: Enable this flag when your IN clause targets a primary key or unique column and you expect at most one result per value. Do not use it on non-unique columns where multiple rows could match a single value.
Range Definitions
Range definitions declare which entities you're querying. Every variable referenced in your query must have a corresponding range definition:
// Single entity range
$results = $entityManager->executeQuery("
range of p is App\\Entity\\ProductEntity
retrieve (p)
");Relationship Traversal (Related Ranges)
To query related entities, use the via keyword to traverse relationships. You always reference the property on the source entity that defines the relationship — ObjectQuel handles the underlying join logic automatically. The syntax is identical regardless of relationship type (ManyToOne, OneToMany, etc.).
Traversing to Related Entities
// ManyToOne: OrderEntity has a 'user' property referencing UserEntity
$results = $entityManager->executeQuery("
range of o is App\\Entity\\OrderEntity
range of u is App\\Entity\\UserEntity via o.user
retrieve (o, u.email) where o.createdAt > '2024-01-01'
");
// OneToMany: UserEntity has an 'orders' property (collection of OrderEntity)
$results = $entityManager->executeQuery("
range of u is App\\Entity\\UserEntity
range of o is App\\Entity\\OrderEntity via u.orders
retrieve (u.name, o.total) where o.status = 'completed'
");In the first example, via o.user follows OrderEntity's user property to reach the related UserEntity. In the second, via u.orders follows UserEntity's orders collection to reach OrderEntity.
Deep Relationship Traversal
Chain multiple via clauses to traverse through several relationship levels. Each range declaration connects to the previous entity through its relationship property:
// Traversal path: User → Orders → Order Items
$results = $entityManager->executeQuery("
range of u is App\\Entity\\UserEntity
range of o is App\\Entity\\OrderEntity via u.orders
range of i is App\\Entity\\OrderItemEntity via o.items
retrieve (u.name, i.quantity) where i.productId = 123
");Retrieving Data
The retrieve clause specifies what data to return. You have three options, each suited to different use cases:
1. Retrieve Full Entities
Returns complete entity objects with all properties hydrated. Use this when you need the entire entity:
$results = $entityManager->executeQuery("
range of p is App\\Entity\\ProductEntity
retrieve (p) where p.active = true
");
foreach($results as $row) {
$product = $row['p']; // Full ProductEntity object
echo $product->getName();
echo $product->getPrice();
}2. Retrieve Specific Properties
Returns only the requested property values as scalars. Use this to minimize memory usage and improve performance:
$results = $entityManager->executeQuery("
range of p is App\\Entity\\ProductEntity
retrieve (p.name) where p.active = true
");
foreach($results as $row) {
$name = $row['p.name']; // String value, not an object
echo $name;
}3. Mix Entities and Properties
Combines full objects with specific property values. Use this when you need complete entities from one range but only specific fields from related entities:
$results = $entityManager->executeQuery("
range of p is App\\Entity\\ProductEntity
range of c is App\\Entity\\CategoryEntity via p.category
retrieve (p, c.name) where p.price < 100
");
foreach($results as $row) {
$product = $row['p']; // Full ProductEntity object
$categoryName = $row['c.name']; // Category name as string
}Filtering with Where Clauses
Build complex conditions using comparison operators and logical combinators:
Comparison Operators
// Range queries
$results = $entityManager->executeQuery("
range of p is App\\Entity\\ProductEntity
retrieve (p) where p.price >= :minPrice and p.price <= :maxPrice
", ['minPrice' => 10.00, 'maxPrice' => 50.00]);
// Alternative using BETWEEN
$results = $entityManager->executeQuery("
range of p is App\\Entity\\ProductEntity
retrieve (p) where p.price between :min and :max
", ['min' => 10.00, 'max' => 50.00]);IN and NOT IN
// Match multiple values
$results = $entityManager->executeQuery("
range of p is App\\Entity\\ProductEntity
retrieve (p) where p.categoryId in (:categories)
", ['categories' => [1, 2, 3]]);
// Exclude multiple values
$results = $entityManager->executeQuery("
range of p is App\\Entity\\ProductEntity
retrieve (p) where p.status not in (:excluded)
", ['excluded' => ['deleted', 'archived']]);NULL Handling
// IS NULL
$results = $entityManager->executeQuery("
range of u is App\\Entity\\UserEntity
retrieve (u) where u.deletedAt is null
");
// IS NOT NULL
$results = $entityManager->executeQuery("
range of u is App\\Entity\\UserEntity
retrieve (u) where u.emailVerifiedAt is not null
");Parameter Binding
Always use parameter binding to prevent SQL injection and enable query plan caching.
// Single parameter
$results = $entityManager->executeQuery("
range of p is App\\Entity\\ProductEntity
retrieve (p) where p.price < :maxPrice
", ['maxPrice' => 100.00]);
// Multiple parameters
$results = $entityManager->executeQuery("
range of p is App\\Entity\\ProductEntity
retrieve (p) where p.price between :min and :max
", [
'min' => 10.00,
'max' => 100.00
]);Sorting Results
Control result ordering with the sort by clause. When specifying multiple fields, they are evaluated left-to-right as tie-breakers:
// Single field
$results = $entityManager->executeQuery("
range of p is App\\Entity\\ProductEntity
retrieve (p) where p.active = true
sort by p.name asc
");
// Multiple fields (primary sort: featured, then price, then name)
$results = $entityManager->executeQuery("
range of p is App\\Entity\\ProductEntity
retrieve (p) where p.active = true
sort by p.featured desc, p.price asc, p.name asc
");
// Sort by related entity properties
$results = $entityManager->executeQuery("
range of p is App\\Entity\\ProductEntity
range of c is App\\Entity\\CategoryEntity via p.category
retrieve (p) where p.active = true
sort by c.name asc, p.name asc
");Pagination
Handle large result sets using the window operator, which provides page-based access to results. ObjectQuel calculates the offset as page_number × items_per_page, so window 0, 10 retrieves items 1–10, window 1, 10 retrieves items 11–20, and window 2, 25 retrieves items 51–75.
// Syntax: window [page_number], [items_per_page]
// Page numbers are 0-indexed (first page = 0)
// First page, 10 items per page
$results = $entityManager->executeQuery("
range of p is App\\Entity\\ProductEntity
retrieve (p) where p.active = true
sort by p.name asc
window 0, 10
");
// Third page, 25 items per page (items 51–75)
$results = $entityManager->executeQuery("
range of p is App\\Entity\\ProductEntity
retrieve (p) where p.active = true
sort by p.name asc
window 2, 25
");sort by clause, the database may return rows in an unpredictable order, causing items to shift between pages or appear more than once.